
Every object existing in nature consists of very small particles known as Atom. Every atom consists of positive and negative charges. The positive charge is known as Proton and negative charge is known as Electron. The number of electrons varies from material to material. The protons are situated at the center of atom along with Neutrons called Nucleolus. While the electrons move around the protons in circular orbit. It is the movement of these electrons, which constitute an Electric Current either through conductor, or space of vacuum when some pressure is applied.
Figure: ATOM
ELECTRIC VOLTAGE:
Voltage or Electro Motive Force (EMF) is a pressure, when applied to a conductor, causes an electric CURRENT to flow. This pressure is generated by an electric Generator, or taken from a Battery cell or from house supply.
This Voltage is measured in terms of VOLTS. The smaller units of Volt are mili volt (mV) and microvolt. 1000 Micro Volt =1 milli Volt (mV); 1000 Volt = 1Kilo Volt (KV); 1000 milli Volt=1 Volt. (V); 1000 Kilo Volt =1 Mega Volt. (MV)
ELECTRIC CURRENT:
Current is nothing but, the number of electrons in a conductor flowing from one point to another point in a given time. The Current is measured in terms of AMPERE. The lower units are milli ampere and micro ampere. 1000 micro Ampere = 1 milli Ampere. (m A); 1000 milli Ampere = 1 Ampere.(A).
The materials, which allow electric current to flow easily without restriction are known as conductors. E.g.: Copper, Gold, Iron Water Etc.
Materials, which do not allow electric current readily, are called non-conductors.
E.g.: dry wood, paper, mica, plastic etc.
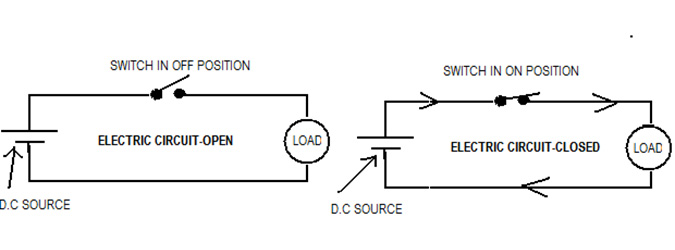
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT:
When a Resistance or any Electrical Apparatus like a electric lamp is connected to a source of supply along with a controlling device such as ‘Switch’, it forms an electric circuit.
ELECTRIC ENERGY/ POWER:
The Power is the amount of Electric Energy consumed by an electric apparatus in a given time. Power is the product of Voltage (V) and Current (I). The power is measured in terms of ‘Watts’. Smaller Units are 1000 Micro Watts = 1 Mili Watts (mW); 1000 Mili Watts =1 Watts. Larger Units are : 1000 Watts = 1 Kilo Watts (KW); 1000 Kilo Watts =1 Mega Watts (MW).
Note: Thus Power(P) = Current(I) X Voltage(V), i.e. P = VI